Building Strategic Advantage: Lessons for AI Startups from 7 Powers
Artificial intelligence is transforming industries at a breathtaking pace, creating vast opportunities for startups to innovate and capture value. However, rapid technological advancements and low barriers to entry also mean that competition in the AI space is fierce. To succeed, AI startups must go beyond building groundbreaking technology—they need to develop sustainable competitive advantages.
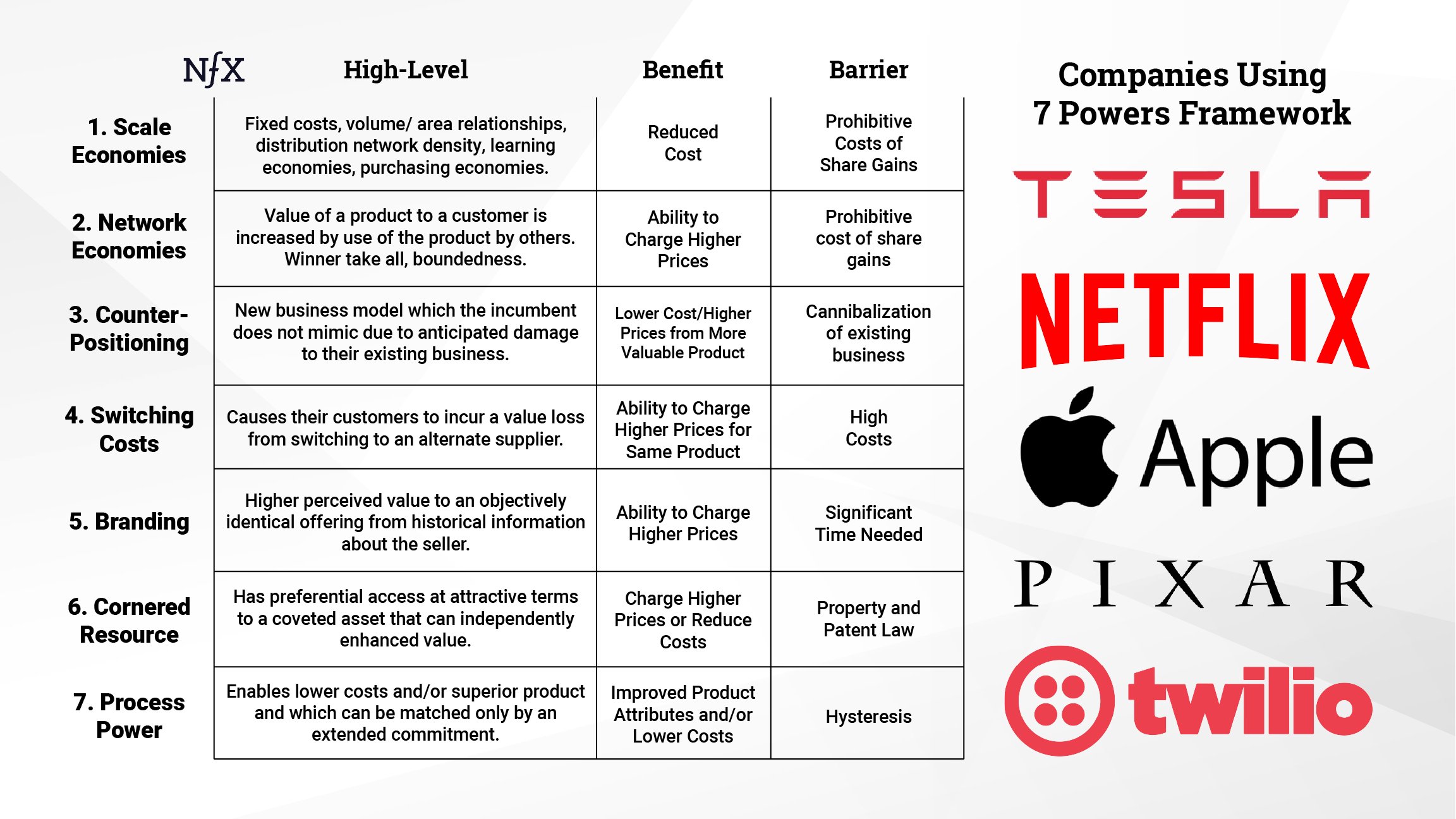
Hamilton Helmer’s 7 Powers: The Foundations of Business Strategy provides a timeless framework for building enduring business success. By adapting Helmer’s seven powers to the AI startup landscape, founders can craft strategies that ensure long-term dominance in this fast-evolving market.
1. Scale Economies: Winning by Being Bigger and Cheaper
In AI, scale economies are especially potent because AI models improve with more data. Larger startups can leverage their access to vast datasets, reducing the per-unit cost of model training while increasing accuracy and utility. Startups that establish scale economies can outcompete smaller rivals on pricing and performance.
How to Apply:
Partner with large organizations to gain exclusive access to proprietary datasets.
Optimize infrastructure costs by investing in scalable cloud solutions and cutting-edge model training techniques.
Offer free or low-cost services initially to grow a user base and collect valuable data for improving your algorithms.
Example: OpenAI’s GPT models gain increasing value as more users interact with them, fueling data collection and refinement at scale.
2. Network Economies: The More, the Merrier
AI platforms thrive on network effects. The more users engage with your platform, the better the outcomes for all participants, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of growth. For instance, marketplaces powered by AI—connecting users, vendors, or developers—become more valuable as they scale.
How to Apply:
Create a two-sided platform, such as an AI-powered talent marketplace or API ecosystem, where both sides benefit from increased participation.
Incentivize early adoption with freemium models or rewards for referrals.
Use community-building tools to enhance engagement and lock in users.
Example: Hugging Face’s AI developer community benefits from shared models and datasets, increasing its value with every contributor.
3. Counter-Positioning: Disrupting the Incumbents
AI startups have a unique opportunity to deploy innovative business models that established players cannot easily replicate without sacrificing their core operations. For example, incumbents in healthcare or finance may struggle to adopt an AI-first approach due to regulatory constraints or entrenched processes.
How to Apply:
Identify where incumbents are slow or resistant to adopting AI and build solutions tailored to those gaps.
Focus on speed, agility, and customer-centric design to outmaneuver larger competitors.
Target underserved niches where traditional solutions fall short, then expand into broader markets.
Example: Lemonade disrupted the insurance industry with AI-driven claims processing, offering faster, cheaper, and more user-friendly services.
4. Switching Costs: Locking in Customers
AI startups can create high switching costs by deeply integrating their technology into customers’ workflows. When customers rely on your AI for mission-critical tasks, the cost and effort of switching to another provider become prohibitive.
How to Apply:
Build products that become indispensable by solving key pain points for your customers.
Offer customization and integration services to embed your AI deeply into client operations.
Use subscription-based pricing models to incentivize long-term commitments.
Example: Salesforce’s AI tools for CRM systems are so embedded in customer workflows that switching to another platform would be disruptive and expensive.
5. Branding: Owning the AI Conversation
In a crowded AI marketplace, a strong brand can differentiate your startup and attract customers, investors, and talent. Branding in AI isn’t just about a logo or tagline—it’s about establishing trust and credibility in delivering cutting-edge, reliable solutions.
How to Apply:
Publish research papers, participate in conferences, and build thought leadership in your domain.
Showcase real-world success stories and testimonials from prominent customers.
Invest in content marketing to explain your technology in accessible, relatable terms.
Example: DeepMind’s brand is synonymous with AI excellence, built through its groundbreaking research and high-profile achievements like AlphaGo.
6. Cornered Resource: Securing Unfair Advantages
Cornered resources in AI could include exclusive datasets, patented algorithms, or unique talent. By securing assets that others can’t replicate, your startup gains a significant edge over competitors.
How to Apply:
Pursue partnerships with industry leaders to co-develop proprietary datasets.
Protect intellectual property with patents and trade secrets.
Attract top AI talent by fostering a culture of innovation and offering meaningful equity stakes.
Example: Tesla’s vertically integrated AI ecosystem, including proprietary FSD (Full Self-Driving) algorithms and in-house chips, is a key competitive advantage.
7. Process Power: Scaling Operational Excellence
AI startups that develop superior processes for model development, deployment, and iteration can outperform competitors. These processes should emphasize efficiency, reproducibility, and rapid adaptation to changing market needs.
How to Apply:
Invest in automation to reduce manual effort in data preprocessing, model training, and deployment.
Develop robust MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) pipelines to ensure continuous delivery and improvement of AI models.
Document and refine internal processes to maintain quality as you scale.
Example: Google’s AI teams leverage highly efficient infrastructure and operational practices to deploy innovations at scale, such as in search and recommendation systems.
Integrating the Powers: A Unified Strategy for AI Startups
Success in the AI industry rarely comes from relying on a single power. The most successful startups integrate multiple powers into a cohesive strategy. For instance, an AI platform might combine network economies (a vibrant developer ecosystem), scale economies (large datasets), and switching costs (deeply embedded tools) to create a competitive fortress.
Steps to Build Your Strategy:
Diagnose Your Market: Identify the specific powers most applicable to your industry and business model.
Align Your Resources: Focus your team, funding, and partnerships on developing these powers.
Defend Your Position: Continuously strengthen your powers to maintain your competitive edge as your company scales.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of AI, technological innovation is just the starting point. To achieve enduring success, startups must master the strategic principles outlined in 7 Powers. By focusing on creating and sustaining competitive advantages—whether through scale, networks, branding, or other powers—AI startups can navigate the challenges of a crowded market and build businesses that thrive for the long term.
With a deliberate and disciplined approach to strategy, your AI startup can become not just a disruptor but a leader in the next phase of the information age.